The Forrester Wave™: Cybersecurity Risk Ratings Platforms, Q2 2024
A security rating (also known as a cybersecurity rating) is a quantifiable measurement of an organization’s security posture, enabling insightful and data-driven decisions around the security performance of an organization and their third-party vendors. SecurityScorecard offers easy-to-understand A-F security ratings driven by ten groups of risk factors.
As the economy moves from a physical to a digital environment, businesses need to change the questions they ask when considering working with vendors, partners, and others in their supply chain or ecosystem. Historically, companies referred to Dun and Bradstreet asking, “What is a good credit score?”
Now many companies are asking the question, “What is a good security score?“
What are cybersecurity ratings?
Cybersecurity ratings are metrics used to assess the overall cybersecurity posture and risk of an organization. In a digital world, data and your company’s protection of that data parallels your income and protection of financial assets.
Consumer credit reporting agencies review a company’s financials and assign a credit score by evaluating whether the company can protect its financial assets and keep from going into debt. Similarly, a security ratings organization reviews a company’s security posture and assigns a security score by evaluating whether the company can protect its data assets from data breaches.
In both of these cases, the ratings organization compares assets and liabilities to provide a score that others can rely on and factor into their decision-making process.
A good security rating is an organizational asset that can open business opportunities and partnerships and provide assurance to existing customers. Poor security rating places can indicate that an organization’s data is at risk. Just as credit ratings provide insight into organizational financial stability, cybersecurity ratings provide insight into the cybersecurity health and practices of an organization.
Why are security ratings important?
Security ratings help organizations better understand the cyber threats they face by offering continuous visibility into internal security postures. Security ratings also aid in compliance efforts as they allow businesses to continually monitor their adherence to regulations that relate to their daily operations. This means that traditional, time-consuming methods of assessing organizational and third-party security risks are removed and businesses can accurately evaluate the strength of their cybersecurity controls.
Traditional methods of assessing organizational and third-party security are time-consuming and resource-intensive. This means that without an adequate budget and staff, many organizations are unable to accurately evaluate the strength of their cybersecurity controls. Security ratings address this challenge by offering continuous visibility into internal security postures, helping organizations better understand the cyber threats they face. Security ratings also aid in compliance efforts as they allow businesses to continually monitor their adherence to regulations that relate to their daily operations.
How are security ratings calculated?
Security ratings take into account the levels of risk that exist within an organization and rate risk based on the category and severity. When calculating security ratings, SecurityScorecard evaluates all external-facing discoverable assets of an organization, the risks associated with those assets, and the severity of the threats they pose. In addition, our scoring algorithm uses a statistical framework that takes into account the millions of rated companies on the SecurityScorecard platform.
Each score is developed based on how many standard deviations an organization is – better or worse – than the average number of risk findings for an organization of the same size. This enables fair comparisons of an organization’s cybersecurity hygiene, helping to improve accuracy, transparency, and fairness to the security rating process.
How to choose a security ratings provider
The needs of your organization will help drive the decision for a security provider. Decision factors can include attack surface size, the size of an organization’s vendors, network size, and service options for each provider. You will want to have a strong grasp on your cybersecurity environment in order to better align with a security ratings provider.
Beyond that, it is important to consider what your organization views as important, such as a seamless customer experience, or the amount of experience a provider has. These factors will come into play as you consider your security ratings provider options.
What can a security rating do for service providers?
Service providers need to prove information security controls and security performance to prospective customers. While SOC reports and certifications offer prospects and customers some information about corporate security posture, these point-in-time assessments have limitations.
A strong security rating offers your customer base up-to-date, objective, and continuous validation that your cybersecurity posture and practices are structured to keep data safe. Organizations can leverage security ratings to help increase profitability. In 2017, news of the Equifax and Kaspersky data breaches put customers on high alert for poor cybersecurity. Providing potential customers independent, validated proof using security ratings offers organizations the opportunity to build the confidence that generates customer loyalty and, thus, profitability.
What does a security rating do for third-party risk management?
Companies looking to hire vendors need security posture assurance often as a part of the procurement process. There is a widespread understanding that outsourcing work does not translate to outsourcing risk and that vetting of the cybersecurity posture of a potential vendor is a requirement, and increasingly a compliance mandate.
The highest security rating is an “A,” indicating a low number of vulnerabilities, threat indicators, and issues; the ratings descend as the severity and number of threat indicators increases. Companies with an F rating are 13.8 times more likely to be victims of data breaches than those with an A rating.
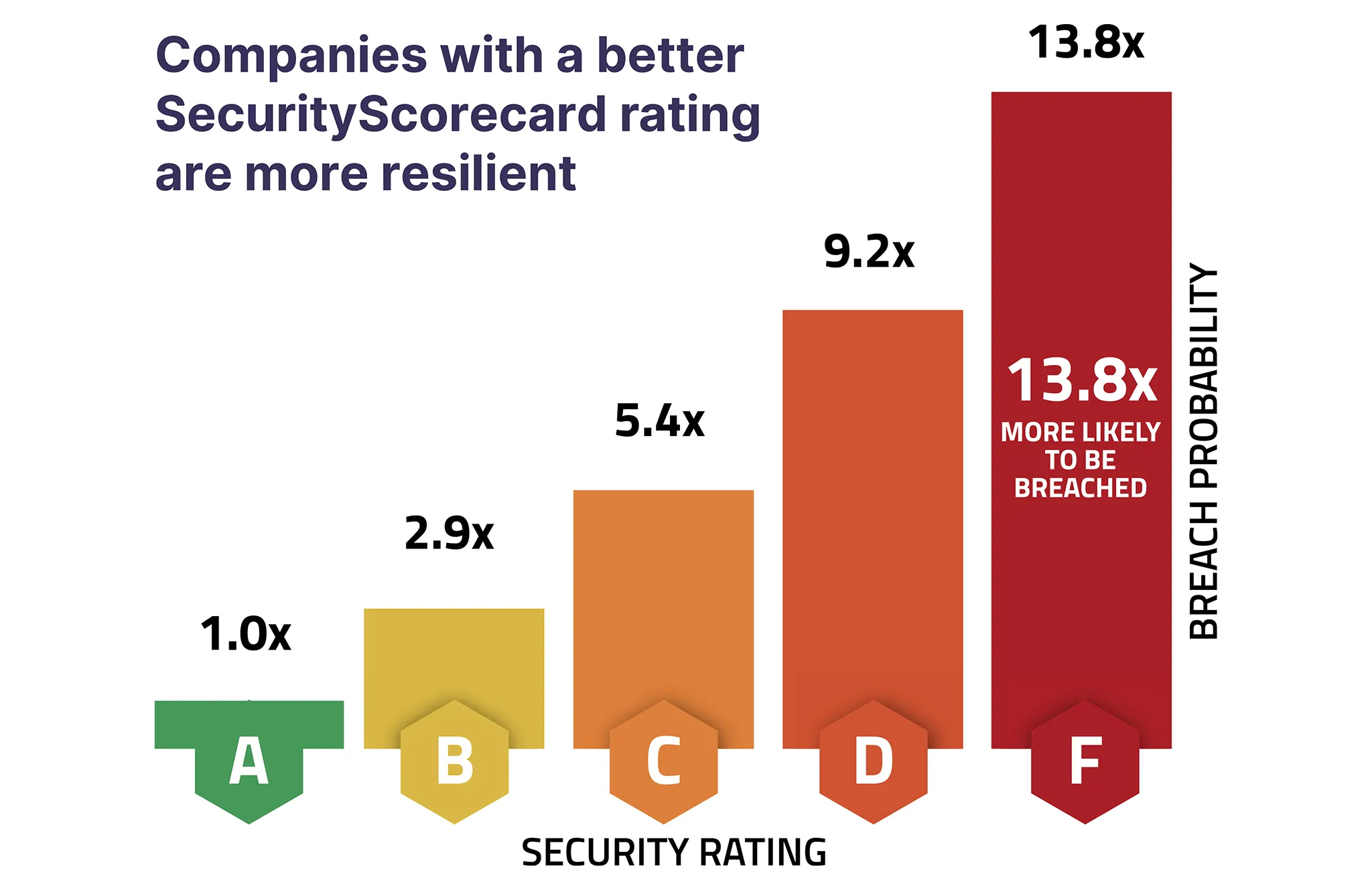
Utilizing security ratings can help prioritize remediation amongst existing third parties, define mandatory thresholds for cybersecurity for new vendors, aid in making decisions in the procurement process, and help define the level of assessment required for each vendor. For example, vendors with an A or B rating provide greater safety to your organization, so organizations may feel more comfortable moving forward with these vendor contracts compared to those vendors with lower grades. Using security ratings, organizations are able to:
- Automate information gathering processes to gain an understanding of vendor security posture.
- Evaluate vendor security practices against their industry standards, helping you identify which vendors pose a significant risk.
- Assess vendor compliance standards against industry standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, and Sarbanes Oxley.
While other sources of information such as references, audit reports, and certifications provide some indication of cybersecurity, these data points are an incomplete picture and cannot provide insight into the strength of day-to-day cybersecurity practices.
What high severity vulnerabilities put businesses at risk?
Security ratings incorporate daily activities such as security monitoring, network security, and endpoint security.
SecurityScorecard technologies rate companies across 10 Risk Factors including application security, network security, DNS health, patching cadence, endpoint security, IP reputation, web application security, cubit score, hacker chatter, leaked credentials, and social engineering. Our platform enables you to drill down into specifics within each factor, giving you the most granular view of how your ecosystem is performing.
A closer look at network security
SecurityScorecard’s security rating platform incorporates a review of network security. SecurityScorecard reviews a company’s password strength and firewall rules when creating its security rating. Password strength is one of the most common vulnerabilities that are exploited by hackers.
A closer look at endpoint security
As more employees bring devices with them or work remotely, endpoint security becomes a higher risk. Employee-connected devices, such as smartphones or tablets, that access public internet environments (as employees work remotely) may become infected with the Mirai IoT malware and allow unauthorized access to secured data. Malicious actors increasingly target endpoints with new threats including both file-based and file-less techniques.
SecurityScorecard security ratings provide transparent information not only about potential weaknesses in endpoint security but also specify which IP addresses are impacted. This allows vendors to easily investigate, address, and remediate concerns. This path takes them to an improved risk rating, which can be leveraged to attract new customers.
For companies looking to hire third-party vendors, SecurityScorecard security ratings give insight into how well potential business partners manage third-party risk and internal risks.
How do a company’s cybersecurity capabilities stack up against its competition?
Service providers seeking business growth need to understand how they compare to others in their landscape. Using SecurityScorecard’s platform to review not only your own business but also those in the same space can provide insight into how potential customers view your cybersecurity posture. If your rating is below that of your competitors, taking steps to secure your IP footprint can help you become a more attractive option to potential customers. When your organization’s security rating exceeds that of your competitors, you have an opportunity to leverage that in business negotiations.
Companies seeking to hire vendors need to prove to their Boards of Directors that they have thoroughly vetted new business partners with data-driven, reliable analysis. Performing this analysis with SecurityScorecard’s platform assures the Board, C-suite, and your auditors that they are seeing up-to-date, accurate information, bringing confidence in your due diligence process.
Common use cases for security ratings
Board reporting and auditing
Data and reporting underlie informed decision-making. One weak audit impacts customer, board, and regulator confidence. Since most audits occur annually, a weak report can impact an organization’s profitability for a year.
Security managers can utilize security ratings between audits to prove that new security measures work. SecurityScorecard technologies continuously scan the internet for vulnerabilities and risk signals. This continuous monitoring means that as you incorporate new protection measures, the data analysis engine recalibrates the score. In addition, security ratings can help security and risk leaders:
- Gauge the value of their cybersecurity technology investments.
- Maximize limited resources and prioritize resource allocation.
- Enable data-driven cybersecurity conversations with key stakeholders and board members.
- Set internal security performance benchmarks.
For smaller organizations, SecurityScorecard’s security rating platform provides instantaneous insight that instills confidence in customers and Boards of Directors in the security hygiene of the organization.
Liquidnet, a broker-dealer handling trades that average $1.4 million, shared, “When it comes to security, Liquidnet is a 350-person company that is expected to act like a 35,000-person company.” As a fintech organization heavily regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (US SEC), Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), and a variety of other governing bodies, Liquidnet needs to respond not only to customers but to regulatory authorities who can potentially levy fines for noncompliance. The SecurityScorecard security rating platform provides a one-touch solution examining independent data that proves compliance, not just questionnaires that assert compliance.
Vendor due diligence
Companies hiring third-parties can incorporate the same review to gain confidence in a vendor. If your vendor is at risk, you are at risk. However, if you cannot break that contract immediately, then you might be worried about your organization’s, and your customers’, security.
Using SecurityScorecard allows you to prove your ongoing due diligence to your customers, Board of Directors, and regulators. Mike Belloise of Trinet, a SecurityScorecard customer, noted, “The first thing I do when a new vendor or partner is going to be onboarded is pull up the SecurityScorecard dashboard, type in the URL, and we view the quick and accurate assessment.” Whether during the onboarding process or as a part of ongoing monitoring, using security ratings as part of a third-party risk management program provides organizations with the insight needed to prove due diligence.
Mergers and acquisitions
Both parties to an acquisition need assurance that assets will be well-protected. Poor cybersecurity is a liability, and corporations seek to understand the scope and size of this potential liability.
If you’re looking to sell your company, you need to know what prospective buyers know. If your potential buyer is looking at your security rating, you need to know it, too.
As you work to acquire a new company, you may make requests for certain cybersecurity standards to be met, similar to requesting mitigation work on a potential home after the initial inspection. By monitoring potential acquisitions with SecurityScorecard, organizations can track progress on vulnerabilities, set expectations about the level of cybersecurity required, and help enable potential acquisitions with information that will help to pinpoint security flaws.
How to understand your security posture with SecurityScorecard
Since any company can access their security rating profile at no cost, you can review your cybersecurity rating today with a free, instant scorecard. Understand your security performance easily to protect your business from hackers.
Using SecurityScorecard, organizations can see how they compare across ten categories of risk. This helps your organization identify key risk factors to address across your attack surface. Understanding the threats your organization faces can help improve your security posture and lessen the chance of a breach. Get started with SecurityScorecard’s security ratings today.
Frequently Asked Questions about security ratings
What is the meaning of security rating?
A security rating is an objective measure of an organization’s security posture. Typically they use an easy-to-understand rating system, such as A-F.
What are the different types of security ratings?
Security ratings can differ based on the provider, but all typically involve a system to measure cyber risk.
How do security ratings work?
Security ratings analyze an organization’s entire cybersecurity landscape to identify risk and vulnerabilities in both the organization and third-party vendors.
What is a security risk rating?
A security risk rating assesses an organization’s entire risk landscape and points to vulnerabilities that should be addressed.
What is the rating scale for cyber security?
SecurityScorecard uses an easy-to-understand scale from A-F, with A being the highest, showing a strong security posture, and F being the lowest, indicating a poor security posture.
How do you rate risk in cyber security?
Organizations can rate risk in cyber security by looking across ten risk factors within their organization, including application security, endpoint security, hacker chatter, DNS health, network security, and more. These risk factors will help your organization gain insight into your security posture and identify ways you can improve it.

